 Height Estimator
Height Estimator
"Height Estimator" is an Android application that uses different techniques and sensors of your device to estimate the height of different things, such as trees, buildings, statues, pylons, monuments...
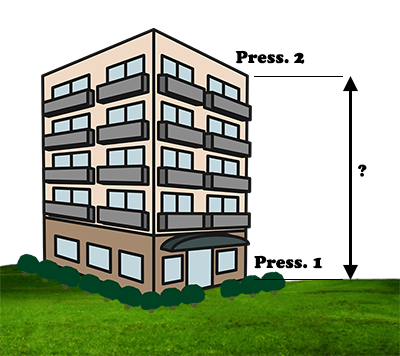
This method is based on the fact that atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. Depending on the model of the smartphone, the accuracy can reach twenty centimeters.
Sensor used: barometer.
One measure of the pressure must be made at the bottom and another at the top.
Measurements can be made indoors or outdoors, but always protected from wind and vibration. During measurements, the smartphone must be placed on a still surface.
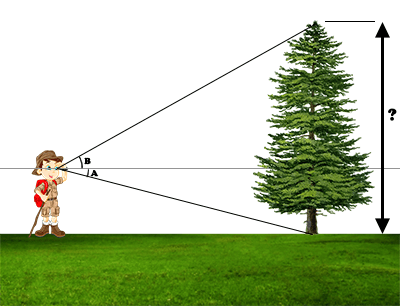
The aim towards the bottom, with a perfectly flat ground, makes it possible to calculate the distance to the object (the height of the eyes must be parameterized in the preferences). The distance being calculated, the aim towards the top makes it possible to estimate the height of the object.
Sensors used: accelerometers (use).
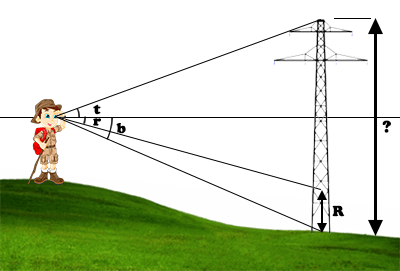
This method is more accurate because the distance to the object should not be estimated. In addition, it works on a floor that is not flat.
In addition to aiming at the base and the top of the object, aim to a known height from the base of the object.
Sensors used: accelerometers (use).
At a given place and time on earth, the position of the sun in the sky is known. By measuring the length of the shadow of an object on a flat ground, one can deduce its height.
Sensor used: GPS (use).
The length of the shadow can be measured:
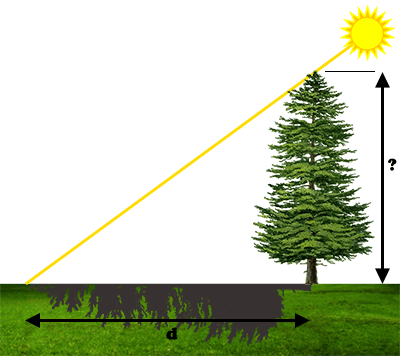
Sensors used: accelerometers (use), possibly GPS (use).
A) If you can go to the target position or locate it on a map, you can use this method.
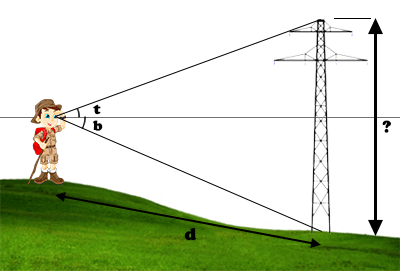
The distance to the target can be measured:
Aiming at the base of the target is only necessary if the ground is not horizontal, to account for the unevenness of the ground.
B) If the target is unreachable and you can not locate it on a map, there is an alternative: to advance in a straight line to the target and to re-measure angles at an intermediate distance.
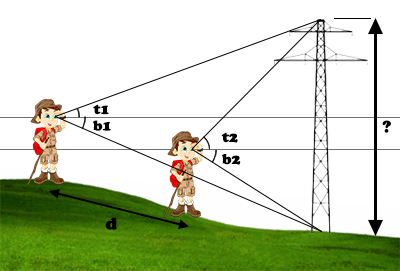
The distance can be measured as before and, again, aim the base only to take into account the altitude difference.
If the target is far away, you are unaware of its position, you can not get there and you can not go in a straight line to it, there is still triangulation...
Sensors used: GPS (use), accelerometers (use), magnetometer (calibration) and gyroscope.
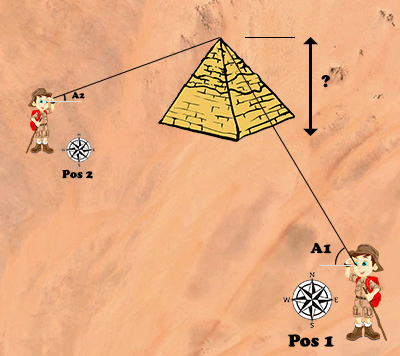
You have to aim the top of the object, from two different GPS positions; the magnetometer is used to determine target directions relative to the north. For better accuracy, point 1, object and point 2 should make an angle approaching 90░.
The two positions as well as the two directions relative to the north make it possible to estimate the position of the object by triangulation. This calculated position can be viewed on a satellite map and possibly corrected on the map.
We can then calculate the distance of the object with respect to points 1 and 2, then, if the ground is flat, estimate the height of the object thanks to the aims made previously.
If the ground is not flat, you can take into account the altitude difference by also aiming at the base of the object from the 2 points.
Another method is to measure how long an object falls. It can be used to estimate the depth of a well, for example. Always be very careful before dropping an object.
Sensor used : chronometer.
Unfortunately, as the following graphs show, the measurement of time must be very precise... Moreover, because of friction in the air, the speed of the fall depends on the object that is dropped. This method is therefore in practice not very precise...
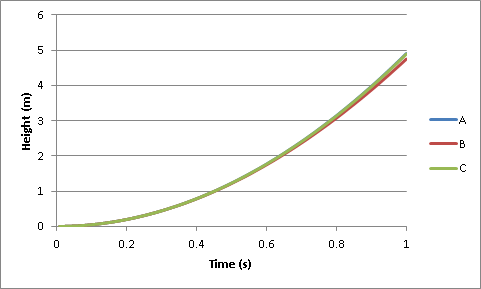
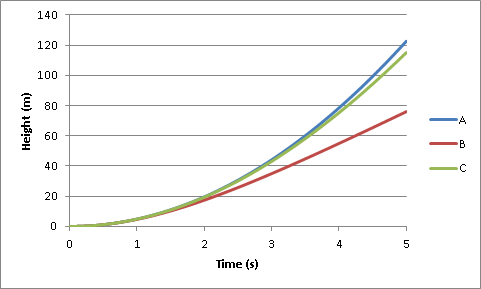
A : neglected friction / B : tennis ball / C : petanque ball
We can measure the time of the fall:
If the measurement is made based on the noise of the impact, the program may take into account the time required for the sound of the impact to arrive at the initial position.
All measurements should be as accurate as possible. No precipitation...
For better accuracy, GPS data is averaged for 10 seconds. It is therefore important to remain still for at least 10 seconds before measuring the position.
You can reset the average by clicking the "Reset GPS averaging / At position" button.
To the right of this button are two precision indicators. The ideal is to have the first less than 5 and the second less than 0.5.
The 3 accelerometers of your smartphone, placed at 90░ relative to each other, allow, thanks to the Earth's gravity, to measure the angle with respect to the horizontal plane.
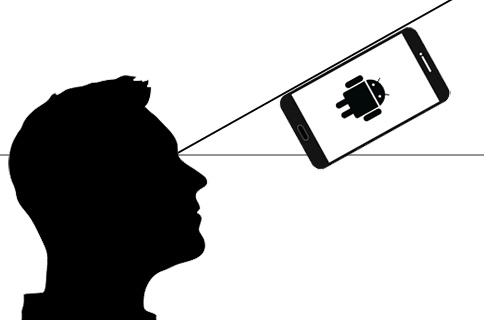
To measure the angle to the horizontal, the program allows two styles of sighting: aiming along the smartphone (preferred method, left) or with the camera (right).

It is very important to calibrate the magnetometer to correctly position the magnetic north. To do this, when the program is in angle and azimuth measurement mode, have "8" movements on your device.
The gyro improves accuracy by measuring the speed of rotation of the smartphone.
To obtain the geographical north, a correction depending on the GPS position is automatically applied by the program.
View and download on the Play Store.
If you want to support the development of the program, and avoid ads, you can donate (minimum 6 EUR or 9 USD).
It's easy and fast. Just click the 'PayPal' button below.
Thanks, Paludour.